 题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
A. industry B. industrial C. instruct D. instruction
A. industry
B. industrial
C. instruct
D. instruction
 如果结果不匹配,请 联系老师 获取答案
如果结果不匹配,请 联系老师 获取答案
 题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
A. industry
B. industrial
C. instruct
D. instruction
 如果结果不匹配,请 联系老师 获取答案
如果结果不匹配,请 联系老师 获取答案
 更多“A. industry B. industrial C. i…”相关的问题
更多“A. industry B. industrial C. i…”相关的问题
Today in Hollywood ______.
A. more television films are produced
B. man-made fighting has completely taken the place of natural light
C. few films are taken for the cinema
D. oil production has become more important than the film industry
A. They can do nothing but give up their outdoor travel.
B. They would feel angry and protest against the ill-trend.
C. The government and the industry may change their attitude.
D. Fewer and fewer urban people will make their seasonal outdoor travel.
使用与练习1相同的信息。
(1)推导厂商的短期供给曲线。(提示:画出成本曲线的基本形状。)
(2)假如市场中有100家相同的厂商,市场供给曲线是怎样的?
Use the same information as in Exercise 1.
a. Derive the firm's short - run supply curve. (Hint: You may want to plot the appropriate cost curves. )
b. If 100 identical firms are in the market, what is the industry supply curve?
企业领导人和决策者往往关切美国产业的“竞争力”(美国产业在世界市场上有盈利地出售自己产品的能力)。
a.汇率的变动如何影响竞争力?
b.假定你想使国内产业更具竞争力。但不想改变总收入。根据蒙代尔—弗莱明模型,你应该采用货币与财政政策的哪一种结合?
Business executives and policymakers are often concerned about the “competitiveness” of American industry (the ability of U.S. industries to sell their goods profitably in world markets).
a.How would a change in the exchange rate affect competitiveness?
b.Suppose you wanted to make domestic industries more competitive but did not want to alter aggregate income. According to the Mundell-Fleming model, what combination of monetary and fiscal policies should you pursue?
Exports are either raw materials or manufactured goods. Raw materials are products of the land, such as cotton, timber or rubber. Some raw materials such as iron ore, come from mines. These raw materials are often exported by the countries that produce them to other countries where they are made into manufactured goods.
Some countries produce food for export, for example, meat, sugar, or cereals such as wheat and maize. These countries are agricultural countries. An agricultural county needs fertile land and a good climate. A cold, dry climate is not suitable for agriculture.
A country which produces manufactured goods is known as an industrialized country. An industrialized country cannot always produce enough food for its own needs. In this case, it does not export foodstuffs. Instead it has to import them. It relies on exports of manufactured products and pays for imports with the money it earns from the exported goods.
21. From the first sentence of the passage we can know that there are()kinds of exports.
A. two
B. three
C. four
22. Raw materials are often exported by the countries that produce them to other countries where().
A. they are consumed
B. they are made into finished products
C. they are wasted
23. The countries which produce food for export,for example, meat, sugar, or cereals such as wheat and maize are()countries.
A. developed
B. industrial
C. agricultural
24. An industrialized country usually has to import foodstuffs because().
A. it cannot always produce enough food for its own needs
B. it doesn't has fertile land and a good climate
C. it relies on exports of manufactured products
25. The best title of this passage is().
A. Agriculture and Industry
B. Export
C. Production
When Bill de Blasio ran for New York City mayor last year, he promised to end a controversial (有争议的), citywide cell-phone ban(禁令)in public schools, which is not equally enforced in all schools. Now, under his leadership, the city is preparing to end the ban. It will be replaced by a policy that allows phones inside schools but tells students to keep them packed away during class.
Many schools have a rule about enforcing the ban that says, “If we don't see it, we don't know about it.” That means teachers are OK with students bringing in cell phones, as long as they stay out of sight and inside bags and pockets.
But at the 88 city schools with metal detectors, die ban has been strictly enforced. The detectors were installed to keep weapon out of schools,but the scanners(扫描器)can also detect cell phones. So students at these schools must leave their phones at home or pay someone to store it for them.
The ban was put into place in 2007 under mayor Michael Bloomberg. Ending the ban will also likely end an industry that has sprung up near dozens of the schools that enforce the ban. Workers in vans(厢式货车)that resemble food tracks store teens' cell phones and Other devices for a dollar a day,
Critics of the ban say cell phones are important safety devices for kids during an emergency. They also say that enforcement of the ban is uneven and discriminatory. Where the ban is enforced, it puts a disadvantage on students who can't afford to pay to store their phones.
Before putting an official end to the cell-phone ban, city education officials are working on creating a new policy. It will include rules about not using the phones during class or to cheat on tests.
1. Which of the following is the main idea of the passage?
A. New York City will give financial aid to poor students.
B. New York City plans to restrict cell phone use in libraries.
C. New York City plans to install metal detectors in all public schools.
D. New York City will soon end a ban on cell phones in schools.
2. Students pay___________ a day to leave their cell phones in a van parked near their school.
A. a dollar
B. two dollars
C. five dollars
D. ten dollars
3. Metal detectors were installed in 88 city schools, mainly to keep ___________ out of schools.
A. cell phones
B. weapons
C. alcohol
D. drugs
4. The word discriminatory in Paragraph 5 probably means ___________.
A. necessary
B. tough
C. strict
D. unfair
5. According to the passage, which of the following statements is TRUE?
A. After the cell-phone ban is ended, students can use their phones during class.
B. The cell-phone ban is equally enforced in all public schools.
C. The cell-phone ban was put into place in 2008 under Mayor Bill de Blasio.
D. A phone-storage industry has appeared outside the 88 metal-detector campuses.
第二篇
Not content with its doubtful claim to produce cheap food for our own population, the factory farming industry also argues that "hungry nations are benefiting from advances made by the poultry(家禽) industry". In fact, rather than helping the fight against malnutrition(营养不良) in "hungry nations", the spread of factory farming has, inevitably aggravated the problem.
Large-scale intensive meat and poultry production is a waste of food resources. This is because more protein has to be fed to animals in the form. of vegetable matte than can ever be recovered in the form. of meat. Much of the food value is lost in the animal' s process of digestion and cell replacement. Neither, in the case of chicken, can one eat feathers, blood, feet or head. In all, only about 44% of the live animal fits to be eaten as meat.
This means one has to feed approximately 9~10 times as much food value to the animal than one can consume from the carcass. As a system for feeding the hungry, the effects can prove disastrous. At times of crisis, grain is the food of life.
Nevertheless, the huge increase in poultry production throughout Asia and Africa continues. Normally British or US firms are involved. For instance, an American based multinational company has this year announced its involvement in projects in several African countries. Britain's largest suppliers of chickens, Ross Breeder, are also involved in projects all over the world.
Because such trade is good for exports, Western governments encourage it. In 1979, a firm in Bangladesh called Phoenix Poultry received a grant to set up a unit of 6,000 chickens and 18,000 laying hens. This almost doubled the number of poultry kept in the country all at once.
But Bangladesh lacks capital, energy and food and has large numbers of unemployed. Such chicken-raising demands capital for building and machinery, extensive use of energy resources for automation, and involves feeding chickens with potential famine- relief protein food. At present, one of Bangladesh' s main imports is food grains, because the country is unable to grow enough food to feed its population. On what then can they possibly feed the chicken?
In this passage the author argues that______。
A. efficiency must be raised in the poultry industry
B. raising poultry can provide more protein than growing grain
C. factory farming will do more harm than good to developing countries
D. hungry nations may benefit from the development of the poultry industry
下表显示了一个以常数边际成本10美元生产的垄断者面临的需求曲线。

(1)计算该厂商的边际收益曲线。
(2)该厂商的利润最大化产量和价格是多少?该厂商的利润为多少?
(3)在一竞争性行业中均衡价格和数量各为多少?
(4)如果该垄断者被迫以完全竞争的均衡价格生产,社会得益是什么?结果是谁获益谁受损?
The following table shows the demand curve facing a monopolist who produces at a constant marginal cost of $ 10.

a. Calculate the firm' s marginal revenue curve.
b. What are the firm's profit - maximizing output and price? What is its profit?
c. What would the equilibrium price and quantity be in a competitive industry?
d. What would the social gain be if this monopolist were forced to produce and price at the competitive equilibrium? Who would gain and lose as a result?
WHY SHOULD YOU ADJUST YOUR HARD HAT SO IT FITS PROPERLY?
_Two colleagues are heading for a construction site._
Robert: Let’s go to the worksite and see the progress.
Ben: OK, you must remember to wear a hard hat.
Robert: {A. You need to check the suspensions regularly,; B. Let me check.; C. That’s really worth noting.; D. Can a hard hat save my life?; E. Thank you for your detailed introduction.}
Ben: Of course. Hard hats are important for protecting your head in open environments.
Robert: Is my hat on properly?
Ben: {A. You need to check the suspensions regularly,; B. Let me check.; C. That’s really worth noting.; D. Can a hard hat save my life?; E. Thank you for your detailed introduction.} First of all, adjust the suspensions.
Robert: I want the hat to fit comfortably so it doesn’t fall off, but I don’t want to make it so tight that it causes discomfort. What should I do?
Ben: You can adjust the chinstraps properly to fit around your chin.
Robert: I see. Do you have any more information about safety?
Ben: {A. You need to check the suspensions regularly,; B. Let me check.; C. That’s really worth noting.; D. Can a hard hat save my life?; E. Thank you for your detailed introduction.} because after years of wear and tear, the entire suspension system may need replacing.
Robert: {A. You need to check the suspensions regularly,; B. Let me check.; C. That’s really worth noting.; D. Can a hard hat save my life?; E. Thank you for your detailed introduction.}
Ben: And do not stuff the gaps of a hard hat or make changes to the hat’s suspension harness. Otherwise, its effectiveness will be impacted.
Robert: {A. You need to check the suspensions regularly,; B. Let me check.; C. That’s really worth noting.; D. Can a hard hat save my life?; E. Thank you for your detailed introduction.} Now I know how important a hard hat is in the high-hazard construction industry!
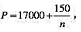 ,n为市场上厂商的数量。设美国和欧洲市场上分别有3亿和5.33亿人口。
,n为市场上厂商的数量。设美国和欧洲市场上分别有3亿和5.33亿人口。a.在没有对外贸易时,美国和欧洲汽车市场上均衡的厂商数量是多少?
b.在没有对外贸易时,美国和欧洲汽车市场上均衡的价格是多少?
c.现在假设美欧之间进行自由贸易,美国市场上除了原有的3亿人口外,将增加5.33亿人口。在美国和欧洲汽车市场上将有多少汽车厂商?汽车新的均衡价格是多少?
d.美国市场上汽车的价格在b和c中为何不同?自由贸易改善了消费者的福利吗?是怎样改善的?
Suppose that fixed costs for a firm in the automobile industry (start- up costs of factories, capital equipment, and so on) are $5 billion and that variable costs are equal to $17,000 per finished automobile. Because more firms increase competition in the market, the market price falls as more firms enter an automobile market, or specifically, where n represents the number of firms in a market. Assume that the initial size of the U.S. and the European automobile markets are 300 million and 533 million people, respectively.
a.Calculate the equilibrium number of firms in the U.S. and European automobile markets without trade.
b.What is the equilibrium price of automobiles in the United States and Europe if the automobile industry is closed to foreign trade?
c.Now suppose that the United States decides on free trade in automobiles with Europe. The trade agreement with the Europeans adds 533 million consumers to the automobile market, in addition to the 300 million in the United States. How many automobile firms will there be in the United States and in Europe combined? What will be the new equilibrium price of automobiles?
d.Why are prices in the United States different in (c) than in (b) ? Are consumers better off with free trade? In what ways?